Monitoring systems with Wazuh. Compliant with NIS2.
Implementing monitoring using the Wazuh platform can be broken down into five key steps that allow you to fully leverage its potential as a unified XDR and SIEM solution. Below is a description of this process, including cloud hosting options:
1. Choosing an implementation model (Cloud vs. On-premises)
The first step is to decide whether the system will be hosted locally or in the cloud. Wazuh Cloud offers managed, ready-to-use, and highly scalable environments for security monitoring and endpoint protection. Choosing the cloud eliminates the need to manage server infrastructure yourself, and users can take advantage of a free trial (Free Cloud Trial) to test the platform. This solution provides protection for public clouds, private clouds, and on-premises data centers.
2. Installation and configuration of the central platform
After selecting a model, you need to install the Wazuh server. This platform is an open source solution, which ensures transparency, flexibility, and no license fees. For self-installation, you can use comprehensive documentation that offers step-by-step guides for users of all skill levels. If you choose the cloud, this step is simplified because the environment is delivered ready to use.
3. Deployment of agents on endpoints
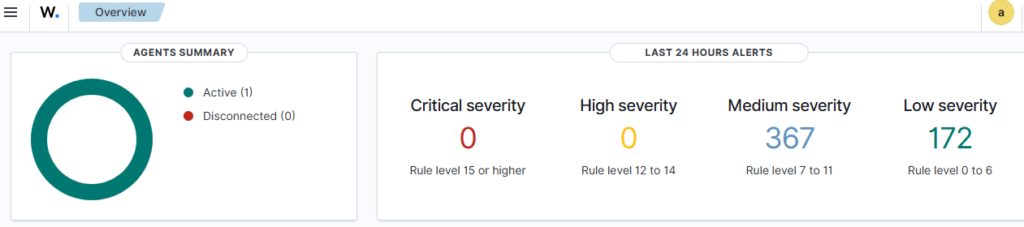
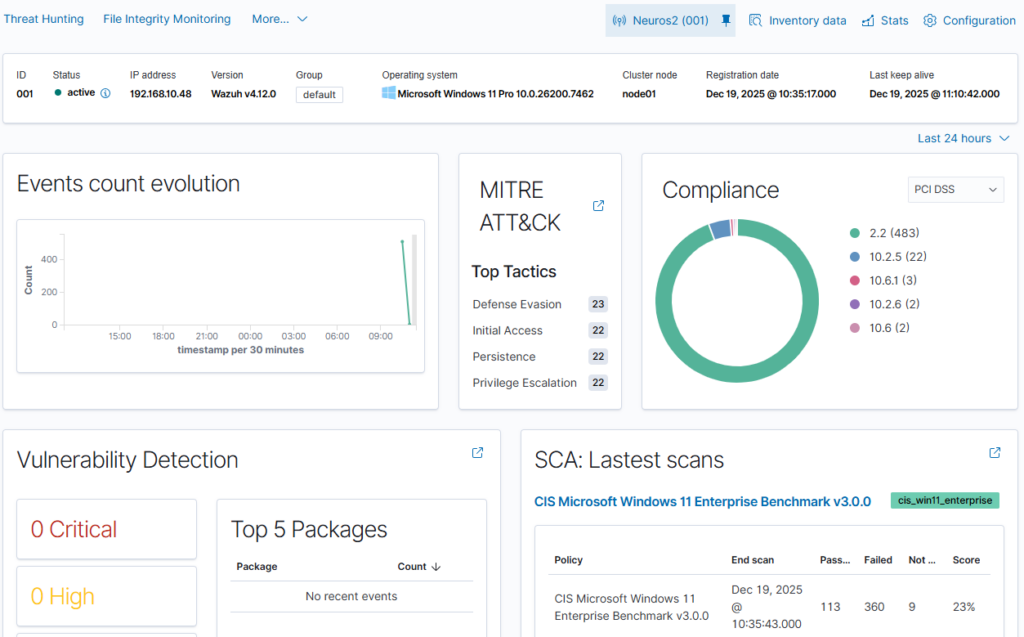
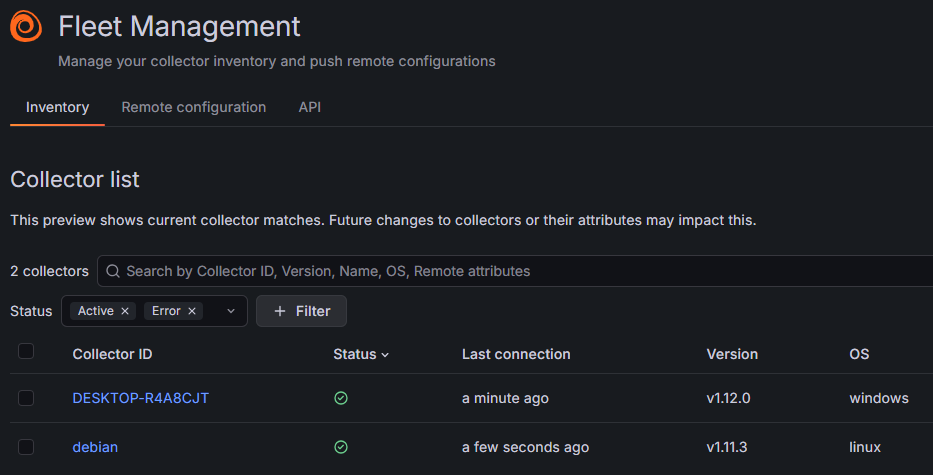
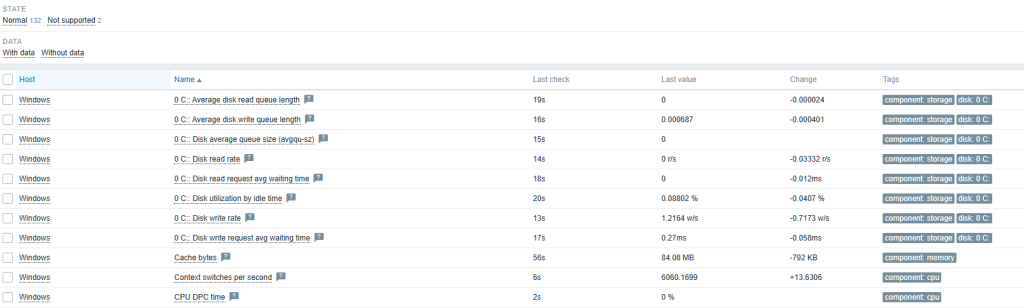
Wazuh uses a single-agent architecture that unifies historically separate functions. Agents must be installed on monitored devices (endpoints) and cloud workloads. These agents are highly flexible and allow you to collect logs and create the necessary alerts.
4. Configuration of protection and detection modules
After connecting the agents to the platform, specific security functions must be configured, such as:
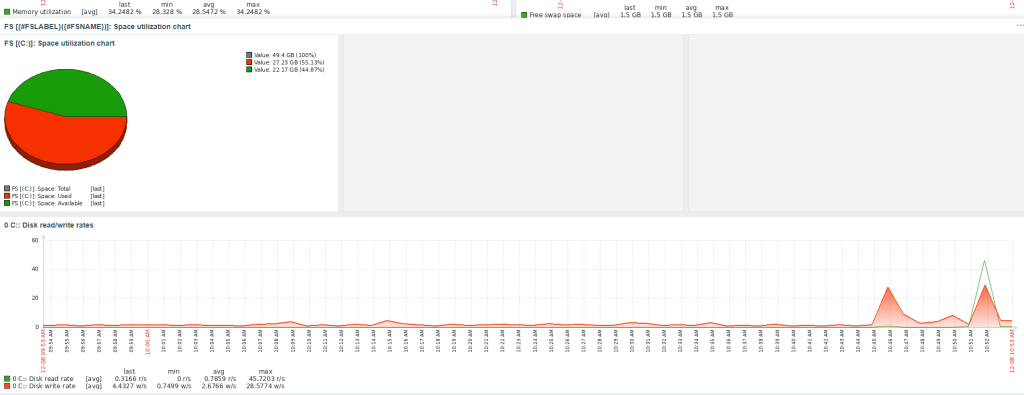
- Endpoint security: File integrity monitoring (FIM), malware detection, and configuration assessment.
- Threat analysis: Vulnerability detection and log data analysis.
- Cloud security: Posture management and container protection.

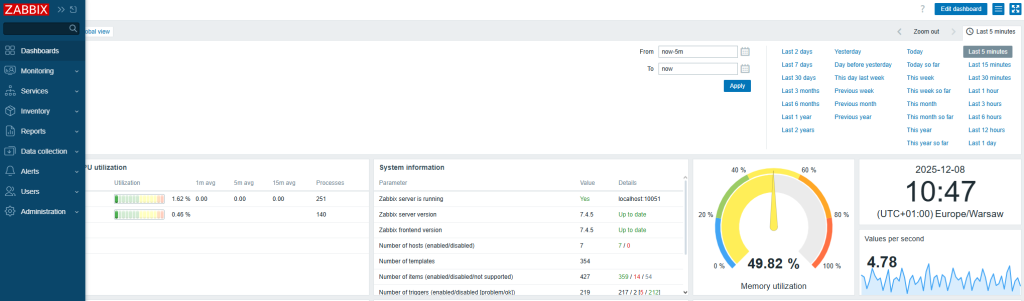
5. Launch security operations and active response
The final step is to configure real-time monitoring and incident response. As a SIEM solution, Wazuh provides monitoring, detection, and notification of security events. With XDR capabilities, the platform provides analysts with real-time data correlation and active responses, which include automatic remediation actions on devices to keep them running smoothly. Integration with external tools such as VirusTotal and PagerDuty is also possible, further enhancing response capabilities.
An analogy for better understanding: Implementing the Wazuh solution can be compared to building a modern building security system. Choosing the cloud (Wazuh Cloud) is like hiring a professional company that provides a ready-made monitoring center, while agents are like smart sensors installed in each room. When a sensor detects smoke or unauthorized entry, the system not only triggers an alarm (SIEM), but can also automatically shut off the gas supply or lock the doors (XDR) to minimize damage.
Monitoring systems with Wazuh. Compliant with NIS2. Read More »