Public Cloud
The public cloud is a platform that uses a standard cloud computing model to make resources such as virtual machines, applications or storage remotely available to users. Public cloud services can be free of charge or offered through various subscription plans or on-demand pricing, including a pay-per-use model.
The most popular public clouds:
- GCP (Google Cloud Partner)
- Azure
- AWS
- Oracle
- IBM
- other (opensource e.g. openstack)
The public cloud model encompasses many different technologies, capabilities and features. However, in essence, the public cloud consists of the following key features:
- on-demand processing and self-service
- pooling of resources
- scalability and rapid flexibility
- pay-per-use pricing
- measured service
- resilience and availability
- security
- broad network access.
A public cloud provider provides the infrastructure needed to host and deploy cloud workloads. It also offers tools and services to help customers manage cloud applications, such as data storage, security and monitoring.
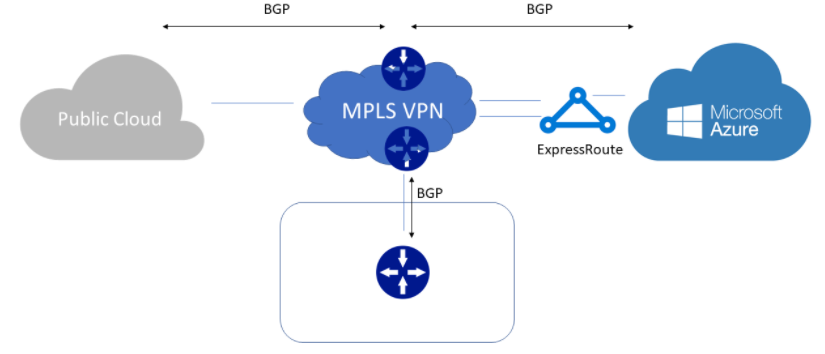
Often, in order to secure the transmission, access to the infrastructure and resources is done via VPN (as below):
Differences in eligibility of expenditure from CAPEX (traditional infrastructure expenditure) to OPEX (maintenance and development).
